Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Rika*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Ota, Hiromichi*; Yamano, Hidemasa
International Journal of Thermophysics, 43(6), p.85_1 - 85_15, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Thermodynamics)In this study, we developed a simple viscosity measurement method based on the principle of least squares to derive the period and logarithmic decrement of oscillation. To confirm the reproducibility of the proposed method, the viscosity of molten nickel was measured and found to be in good agreement with those reported in the literature. The measurement error was less than  3%. Further, the experimental data showed good reproducibility, and the measurements were obtained with high accuracies using the proposed method.
3%. Further, the experimental data showed good reproducibility, and the measurements were obtained with high accuracies using the proposed method.
 C-stainless steel alloys
C-stainless steel alloysNishi, Tsuyoshi*; Sato, Rika*; Ota, Hiromichi*; Kokubo, Hiroki*; Yamano, Hidemasa
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 552, p.153002_1 - 153002_7, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:31.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Determining high precision viscosities of molten B C-stainless steel (B
C-stainless steel (B C-SS) alloys is essential for the core disruptive accident analyses of sodium-cooled fast reactors and for analysis of severe accidents in boiling water reactors (BWR) as appeared in Fukushima Daiichi. However, there are no data on the high precision viscosities of molten B
C-SS) alloys is essential for the core disruptive accident analyses of sodium-cooled fast reactors and for analysis of severe accidents in boiling water reactors (BWR) as appeared in Fukushima Daiichi. However, there are no data on the high precision viscosities of molten B C-SS alloys due to experimental difficulties. In this study, the viscosities of molten SS (Type 316L), 2.5mass%B
C-SS alloys due to experimental difficulties. In this study, the viscosities of molten SS (Type 316L), 2.5mass%B C-SS, 5.0mass%B
C-SS, 5.0mass%B C-SS, and 7.0mass%B
C-SS, and 7.0mass%B C-SS alloys were measured using the oscillating crucible method in temperature ranges of 1693-1793 K, 1613-1793 K, 1613-1793 K, and 1713-1793 K, respectively. The viscosity was observed to increase as the B
C-SS alloys were measured using the oscillating crucible method in temperature ranges of 1693-1793 K, 1613-1793 K, 1613-1793 K, and 1713-1793 K, respectively. The viscosity was observed to increase as the B C concentration increased from 0 to 7.0 mass%. Using the experimental data of the molten 2.5mass%B
C concentration increased from 0 to 7.0 mass%. Using the experimental data of the molten 2.5mass%B C-SS and 5.0mass%B
C-SS and 5.0mass%B C-SS and 7.0mass%B
C-SS and 7.0mass%B C-SS in the temperature range of 1713-1793 K, the equation for the viscosity of molten B
C-SS in the temperature range of 1713-1793 K, the equation for the viscosity of molten B C-SS alloys was determined, and the measurement error of the viscosity of molten B
C-SS alloys was determined, and the measurement error of the viscosity of molten B C-SS alloys is less than
C-SS alloys is less than  8%.
8%.
Ogawa, Shuichi*; Taga, Ryo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Takakuwa, Yuji*
Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology A, 39(4), p.043207_1 - 043207_9, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.86(Materials Science, Coatings & Films)Nickel (Ni) is used as a catalyst for nitric oxide decomposition and ammonia production but it is easily oxidized and deactivated. Clarification of the reduction process of oxidized Ni is essential to promote more efficient use of Ni catalysts. In this study, the reduction processes were investigated by in situ time-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy. We propose a two-step reduction reaction model. The rate-limiting process for the first step is surface precipitation of O atoms and that of the second step is dissociation of H molecules.
molecules.
Doi, Takashi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Surface and Interface Analysis, 52(12), p.1117 - 1121, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:2.52(Chemistry, Physical)Ni-base alloys has been widely used for chemical plants because of their high strength and excellent oxidation resistance. In particular, the addition of Sn and Sb in Ni-base alloys significantly improves the metal dusting resistance. It is indicated that Sn and Sb are segregated on the alloy surface in the metal dusting environment; however, the details have not been clarified yet. The behavior of the Ni-Sn and Ni-Sb alloys under a high-temperature oxidation environment was investigated by in situ X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. It was confirmed that Sn and Sb have been segregated at the surface of their alloys during oxidation in low oxygen potential environment. These results indicate that Sn and Sb segregation improves the metal dusting resistance.
Kado, Rikiya*; Kishi, Tetsuo*; Lelong, G.*; Galoisy, L.*; Matsumura, Daiju; Calas, G.*; Yano, Tetsuji*
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 539, p.120070_1 - 120070_8, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:28.65(Materials Science, Ceramics)Koyanagi, Yoshihiko*; Ueta, Shigeki*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; Cho, K.*; Yasuda, Hiroyuki*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 773, p.138822_1 - 138822_11, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:19.16(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology) C addition on viscosity of austenitic stainless steel in liquid state
C addition on viscosity of austenitic stainless steel in liquid stateOta, Hiromichi*; Kokubo, Hiroki*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.858 - 860, 2019/09
A viscosity measurement apparatus has been developed. It is known that the measurement of the viscosity of molten alloy at elevated temperatures is difficult due to the difficulty of handling for low viscosity fluids such as the stainless steel (SS)+B C alloy. In this study, the viscosities of the molten nickel (Ni) and stainless steel (SS) were measured by the oscillating crucible method to confirm the performance of the viscosity measurement apparatus as a first step. This method is suitable for high temperature molten alloys. A crucible containing molten metal is suspended, and a rotational oscillation is given to the crucible electromagnetically. The oscillation was damped by the friction of molten metal. The viscosity is determined from the period of oscillation and the logarithmic decrement. The crucible was connected to a mirror block and an inertia disk made of aluminum, and whole of them was suspended by a wire made of platinum-13% rhodium alloy. A laser light is irradiated to the mirror. The reflection light is detected by the photo-detectors, and then, the logarithmic decrement of molten metal is determined. The viscosities of molten nickel and SS melts were measured up to 1823 K. In these results, the measured viscosity values of molten Ni and SS were close to those of the literature values of molten Ni and SS. By the equipment, the viscosity of molten SS+B
C alloy. In this study, the viscosities of the molten nickel (Ni) and stainless steel (SS) were measured by the oscillating crucible method to confirm the performance of the viscosity measurement apparatus as a first step. This method is suitable for high temperature molten alloys. A crucible containing molten metal is suspended, and a rotational oscillation is given to the crucible electromagnetically. The oscillation was damped by the friction of molten metal. The viscosity is determined from the period of oscillation and the logarithmic decrement. The crucible was connected to a mirror block and an inertia disk made of aluminum, and whole of them was suspended by a wire made of platinum-13% rhodium alloy. A laser light is irradiated to the mirror. The reflection light is detected by the photo-detectors, and then, the logarithmic decrement of molten metal is determined. The viscosities of molten nickel and SS melts were measured up to 1823 K. In these results, the measured viscosity values of molten Ni and SS were close to those of the literature values of molten Ni and SS. By the equipment, the viscosity of molten SS+B C alloys are measured. The B
C alloys are measured. The B C concentration dependence of the viscosity of molten SS+B
C concentration dependence of the viscosity of molten SS+B C alloys is to be clarified.
C alloys is to be clarified.
Kokubo, Hiroki*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Ota, Hiromichi*; Yamano, Hidemasa
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 82(10), p.400 - 402, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:36.72(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)It is important to obtain the viscosity of a mixed alloy consisting of molten stainless steel and boron-carbide (SUS316L + B C alloy) for the improvement of severe accident assessment methodology for sodium-cooled fast reactors. In this study, the viscosities of the molten nickel (Ni) and stainless steel (SUS316L) were measured by the oscillating crucible method to confirm the performance of the viscosity measurement apparatus as a first step. The viscosities of molten Ni and SUS316L melts were measured up to 1823 K. It was found that the measured viscosity values of molten Ni and SUS316L were estimated from the deviation of the experimental data, were
C alloy) for the improvement of severe accident assessment methodology for sodium-cooled fast reactors. In this study, the viscosities of the molten nickel (Ni) and stainless steel (SUS316L) were measured by the oscillating crucible method to confirm the performance of the viscosity measurement apparatus as a first step. The viscosities of molten Ni and SUS316L melts were measured up to 1823 K. It was found that the measured viscosity values of molten Ni and SUS316L were estimated from the deviation of the experimental data, were  4% and
4% and  3%, respectively. It was also found that those of molten Ni and SUS316L were close to those of the literature values of molten Ni and similar composite stainless steels. Moreover, we tentatively measured the viscosity of molten SUS316L-5 mass%B
3%, respectively. It was also found that those of molten Ni and SUS316L were close to those of the literature values of molten Ni and similar composite stainless steels. Moreover, we tentatively measured the viscosity of molten SUS316L-5 mass%B C alloy. The fitted results of the viscosity for molten Ni and SUS316L were obtained.
C alloy. The fitted results of the viscosity for molten Ni and SUS316L were obtained.
Hasegawa, Mika*; Sugawara, Kenta*; Suto, Ryota*; Sambonsuge, Shota*; Teraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Filimonov, S.*; Fukidome, Hirokazu*; Suemitsu, Maki*
Nanoscale Research Letters, 10, p.421_1 - 421_6, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:52.35(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Graphene has attracted much attention as a promising material in electronics and photonics. The graphitization temperature of 1473 K or higher of graphene-on-silicon(GOS), however, is still too high to be fully compatible with the Si technology. Here, the first application of Ni-assisted formation of graphene to the GOS method was reported. We demonstrate that the graphene formation temperature can be reduced by more than 200 K by this method. Moreover, solid-phase reactions during heating/annealing/cooling procedures have been investigated in detail by using 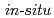 synchrotron-radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. As a result, we clarify the role of Ni/SiC reactions, in which not only Ni silicidation and but also Ni carbonization is suggested as a key process in the formation of graphene.
synchrotron-radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. As a result, we clarify the role of Ni/SiC reactions, in which not only Ni silicidation and but also Ni carbonization is suggested as a key process in the formation of graphene.
Segawa, Tomoomi; Kawaguchi, Koichi; Ishii, Katsunori; Suzuki, Masahiro; Arimitsu, Naoki*; Yoshida, Hideto*; Fukui, Kunihiro*
Advanced Powder Technology, 26(3), p.983 - 990, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:27.86(Engineering, Chemical)Denitration of the aqueous solution of nickel nitrate hexahydrate (Ni(NO )
)
 6H
6H O) by a microwave heating method was investigated. Since Ni(NO
O) by a microwave heating method was investigated. Since Ni(NO )
)
 6H
6H O aqueous solution cannot be heated to over 300
O aqueous solution cannot be heated to over 300  C by microwave irradiation owing to the low microwave absorptivity of its intermediate, NiO could not previously be obtained by microwave heating. We propose a novel NiO synthesis method that uses microwave heating without the risk of chemical contamination. A NiO powder reagent was added to the solution as a microwave acceptor. The denitration efficiency to NiO could be improved by an adiabator around the reactor to increase the temperature homogeneity in the reactor. Numerical simulations also reveal that the use of the adiabator results in remarkable changes in the electromagnetic field distribution in the reactor, temperature inhomogeneity decreases.
C by microwave irradiation owing to the low microwave absorptivity of its intermediate, NiO could not previously be obtained by microwave heating. We propose a novel NiO synthesis method that uses microwave heating without the risk of chemical contamination. A NiO powder reagent was added to the solution as a microwave acceptor. The denitration efficiency to NiO could be improved by an adiabator around the reactor to increase the temperature homogeneity in the reactor. Numerical simulations also reveal that the use of the adiabator results in remarkable changes in the electromagnetic field distribution in the reactor, temperature inhomogeneity decreases.
Fukui, Kunihiro*; Igawa, Yusuke*; Arimitsu, Naoki*; Suzuki, Masahiro; Segawa, Tomoomi; Fujii, Kanichi*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Yoshida, Hideto*
Chemical Engineering Journal, 211-212, p.1 - 8, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:41.13(Engineering, Environmental)The process for synthesizing metallic oxide powders by the microwave denitration method was investigated using hexahydrated nickel nitrate and trihydrated copper nitrate aqueous solutions, and the electrical field and the temperature distributions in the reactor were numerically simulated. Although CuO powder can be obtained from a trihydrated copper nitrate aqueous solution by the microwave denitration method, a hexahydrated nickel nitrate aqueous solution cannot be heated up to over 270  C by microwave irradiation. It was also found that the reaction routes for microwave heating are the same as those for conventional external heating. This finding indicates that the success of producing oxide particles by microwave denitration depends not only on the microwave absorptivity of the intermediate and the metallic oxide, but also on the temperature difference.
C by microwave irradiation. It was also found that the reaction routes for microwave heating are the same as those for conventional external heating. This finding indicates that the success of producing oxide particles by microwave denitration depends not only on the microwave absorptivity of the intermediate and the metallic oxide, but also on the temperature difference.
Yamaguchi, Masatake; Shiga, Motoyuki; Kaburaki, Hideo
Science, 309(5741), P. 1677d, 2005/09
Geng et al. claim in their comment that the segregation energy of sulfur atoms in a nickel grain boundary should be calculated not on average as we did but incrementally. From their own calculations using the incremental binding energies, they concluded that the two-monolayer (GB0 4/4, GB2 4/4) segregation that bring about the reduction of the tensile strength by one order of magnitude has only 1% occupation possibility. However, they miss the point that there are many paths to the (GB0 4/4, GB2 4/4) configuration. In our re-examined calculations, one path has the 50% possibility of the occupation even if we use the incremental binding energies. Furthermore, there may be other paths that have larger possibility. To begin with, Geng et al.'s claims are not meaningful because the prediction of the occupation possibility using the simple McLean's model is not quantitative but qualitative. On the other hand, they claim that another two-monolayer (GB1 4/4, GB2 4/4) configuration brings about the reduction of the tensile strength by one order of magnitude. Their results may be miscalculations, because that is not the case in our re-examined calculations. Furthremore, they suggest a new mechanism of the strong decohesion due to the directional change of the Ni-S bonds. However, they do not show any clear evidence.
Daido, Hiroyuki; Yamaguchi, Naohiro*; Midorikawa, Katsumi*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Moribayashi, Kengo
Reza Handobukku Dai-2-Han, p.325 - 335, 2005/04
no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Masatake; Shiga, Motoyuki; Kaburaki, Hideo
Science, 307(5708), p.393 - 397, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:281 Percentile:98.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Sulfur-induced embrittlement of nickel has long been wrapped in mysteries why and how sulfur weakens the grain boundaries of nickel and why a critical intergranular sulfur concentration is required. From first-principles calculations, we found that a large grain boundary expansion is caused by a short-range overlap repulsion among densely segregated and neighboring sulfur atoms. This expansion results in a drastic grain boundary decohesion that reduces the grain boundary tensile strength by one order of magnitude. This decohesion may directly causes the embrittlement since the critical sulfur concentration of this decohesion agrees well with experimental data of the embrittlement.
 Ni migration through crushed rock media
Ni migration through crushed rock mediaTanaka, Tadao; Sakamoto, Yoshiaki; Mukai, Masayuki; Maeda, Toshikatsu; Nakayama, Shinichi
Radiochimica Acta, 92(9-11), p.725 - 729, 2004/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.03(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Migration experiments of  Ni for crushed rocks, granite and tuff, were performed under the coexistent condition with a humic acid and a fulvic acid of 0-30 mg/l in concentration, which are Nordic humic substances supplied from International Humic Substance Society. Migration experiments of Ni had been performed by a column system, to investigate migration behavior of Ni through a column packed crushed rock. The Ni concentration in the effluent passed through the column was corresponding to the fractional percentage of Ni complexing with humic substance in influent solution. This result suggests that the Ni complexing with humic substance in influent solution was flowed out from the column without any effective interactions with the rock media. The migration behavior of Ni could be expressed by a migration model taking account of the complexation kinetics of Ni with humic substance in the aqueous phase.
Ni for crushed rocks, granite and tuff, were performed under the coexistent condition with a humic acid and a fulvic acid of 0-30 mg/l in concentration, which are Nordic humic substances supplied from International Humic Substance Society. Migration experiments of Ni had been performed by a column system, to investigate migration behavior of Ni through a column packed crushed rock. The Ni concentration in the effluent passed through the column was corresponding to the fractional percentage of Ni complexing with humic substance in influent solution. This result suggests that the Ni complexing with humic substance in influent solution was flowed out from the column without any effective interactions with the rock media. The migration behavior of Ni could be expressed by a migration model taking account of the complexation kinetics of Ni with humic substance in the aqueous phase.
Hotta, Takashi; Dagotto, E.*
Physical Review Letters, 92(22), p.227201_1 - 227201_4, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:80.89(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Ground-state properties of layered nickelates are investigated based on the orbital-degenerate Hubbard model coupled with lattice distortions, by using numerical techniques. The N el state composed of spin
el state composed of spin  =1 ions is confirmed in the undoped limit
=1 ions is confirmed in the undoped limit  =0. At
=0. At  =1/2, novel antiferromagnetic states, called CE- and E-type phases, are found by increasing the Hund's coupling. (
=1/2, novel antiferromagnetic states, called CE- and E-type phases, are found by increasing the Hund's coupling. (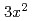

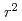 /
/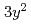

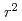 )-type orbital ordering is predicted to occur in a checkerboard-type charge-ordered state. At
)-type orbital ordering is predicted to occur in a checkerboard-type charge-ordered state. At  =1/3,
=1/3, 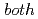 Coulombic and phononic interactions are found to be important, since the former stabilizes the spin stripe, while the latter leads to the striped charge-order.
Coulombic and phononic interactions are found to be important, since the former stabilizes the spin stripe, while the latter leads to the striped charge-order.
Nakamura, Hirofumi; Shu, Wataru; Hayashi, Takumi; Nishi, Masataka
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 313-316(1-3), p.679 - 684, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:72.74(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Tang, H.; Daido, Hiroyuki; Kishimoto, Maki; Sukegawa, Kota*; Tai, R.; Mesesson, S.*; Tanaka, Momoko; Lu, P.; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Nagashima, Keisuke; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 42(2A), p.443 - 448, 2003/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:50.38(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
 NiRuO
NiRuO
Yoshii, Kenji; Abe, Hideki*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Tanida, Hajime*; Kawamura, Naomi*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 348(1-2), p.236 - 240, 2003/01
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:63.77(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Luo, G.-N.*; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Terai, Takayuki*; Yamawaki, Michio*
Surface Science, 505, p.14 - 24, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:20.6(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English